Have you just recently found that you require a hearing aid? There are many details out there when it comes to the different types of hearing aids, and there are numerous different options to choose from. But you don’t know where to start?
While not every style will be the ideal one for you, knowing the distinctions between the types of hearing aids will make the entire process smoother. Learn more about the differences between the types of hearing aids.
Invisible-In-the-Canal (IIC)
One of the tiniest listening devices offered, this type is nearly undetectable. Typically utilized for mild to moderate hearing loss, this hearing aid fits deeply into the ear canal.
Pros:
- Small hearing aid
- Becomes unnoticeable in many ears
- It has enhanced sound quality
- Cosmetic appeal
Cons:
- Due to size, the device can be hard to manage and handle
- It uses tiny batteries, which can pose an issue for those with dexterity concerns
- Batteries need to be changed out more due to size
- Controls are not included on the device
- Susceptible to moisture damage
Completely-In-Canal (CIC)
Among the tiniest listening devices offered, this type of hearing aid consists of a small case that fits into your ear canal.
Pros:
- Among the tiniest listening devices readily available
- Listening devices are among the least noticeable types
- It has enhanced sound quality
- Cosmetic appeal
Cons:
- Short battery life due to size
- Small batteries can be hard to deal with
- Vulnerable to moisture damage
- No controls on the device
- Batteries need to be changed out faster
In-The-Canal (ITC)
Slightly bigger than CIC and IIC styles, this hearing aid is included in a tiny case that suits the lower part of the external ear.
Pros:
- Little enough to be less noticeable in the ear
- Cosmetic appeal
- It can consist of controls on the device
- Larger battery than CIC or IIC types
Cons:
- Despite its small size, hearing aid is still partially visible
- Controls on gadgets might be challenging to handle for those with dexterity problems
- Prone to water damage
- It can make users feel “plugged up.”
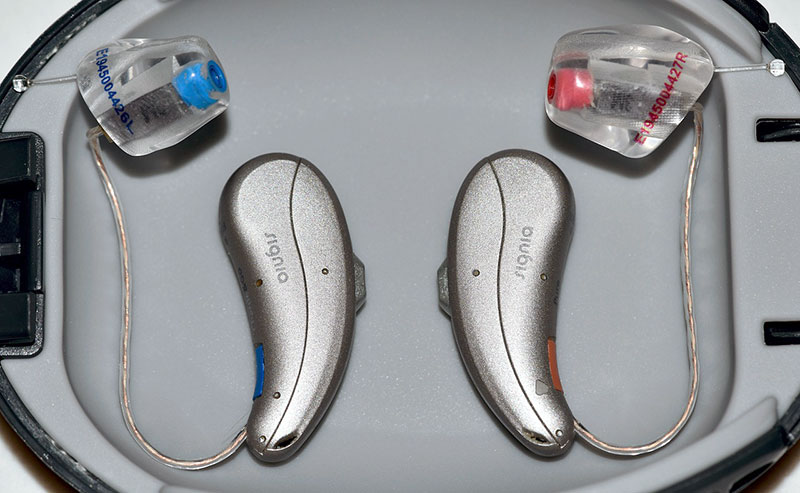
Receiver-In-Canal (RIC)
This kind of listening device looks similar to behind-the-ear listening devices, but the speaker is put inside the ear canal with this design.
Pros:
- Smaller in size
- More discreet than BTEs
- Comfy fit
- Natural sound quality
- Long battery life
Cons:
- Speaker is vulnerable to clogging up
- Small size can be challenging for those with dexterity problems
- Speaker is vulnerable to water damage
In-The-Ear (ITE)
Larger than canal aids, this type of listening device is simpler to deal with for some individuals. With in-the-ear aids, all parts are contained within the shell sitting in the ear’s outer region.
Pros:
- Longer battery life due to bigger battery size
- Controls can be located on the device
- Easy to deal with
Cons:
- Device is visible in the ear
- Sensitive to wind and external noise due to size
Behind-The-Ear (BTE)
With this style, all of the hearing aid parts are contained and stays behind the ear, offering cosmetic and listening advantages.
Pros:
- Good choice for those with dexterity problems
- Large external controls
- Long battery life
- Resilient
- Less vulnerable to moisture or earwax
Cons:
- The listening device is not discreet
- It can make users feel “plugged up.”
- Can hinder eyeglasses