Otitis media, more generally understood as an ear infection, is a prevalent medical condition among children. It has been estimated that more than 80% of children will develop at least one ear infection by the age of three. Ear infections in children can cause notable discomfort and give rise to complications ranging from fever to a damaged eardrum. However, prompt medical attention can provide effective treatment for the condition.
It is recommended that parents seek medical attention for their children if they suspect that their child may be suffering from an ear infection. By doing so, they can mitigate the potential complications associated with the condition and alleviate the discomfort experienced by their child.
Ear Infections in Children: When is it Time to See a Doctor?
The ear is a complicated organ that can be subdivided into three main parts: the outer, middle, and inner parts of the ear. The outer ear is the visible portion of the ear that sits outside the head, along with the ear canal. The middle ear is located inside the head, behind the eardrum, which is a thin membrane that stretches across the end of the ear canal and plays a vital role in perceiving sounds. The inner ear, on the other hand, is situated deep inside the head and is responsible for detecting sound and sending electrical signals to the brain.
Middle ear infections are a prevalent medical condition. Typically, such infections arise due to bacteria or viruses in the middle ear, leading to inflammation, pressure, and pain, as the eardrum is highly sensitive. The accumulation of pus and fluid in the middle ear is responsible for these symptoms.
The eustachian tubes are responsible for draining excess fluid from the ears. However, swelling of these tubes caused by infections, acid reflux, or allergies can impede proper mucus drainage. Children are at a higher risk of developing ear infections since they have flatter eustachian tubes that hinder drainage compared to adults.
Symptoms of an Ear Infection
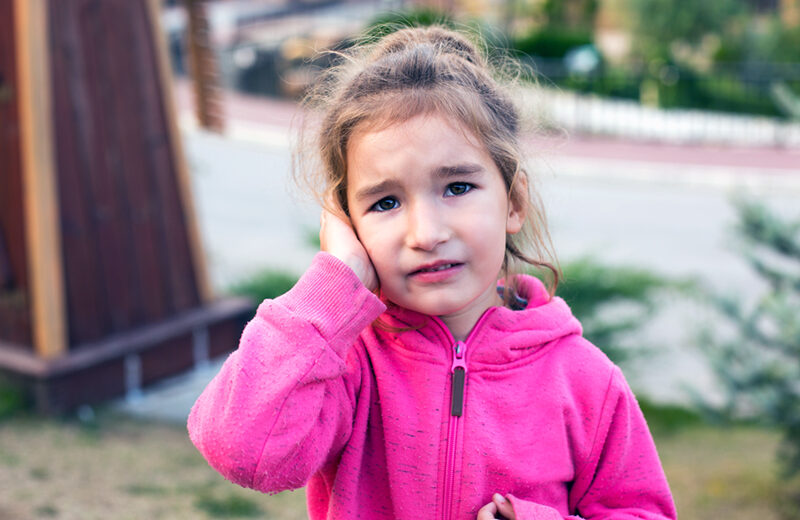
Ear pain and pressure on the eardrum are the most prominent symptoms of a middle ear infection. Pressure changes in the middle ear can cause discomfort while eating, drinking, or sleeping. If the pressure becomes too high, it can rupture the eardrum, leading to fluid drainage. Additional symptoms may include dizziness, nausea, and ringing or buzzing in the ear. You should seek medical attention if your child experiences any of these symptoms.
Middle ear infections are a common occurrence and usually resolve on their own within 2-3 days. However, if the symptoms persist or you have an infant or toddler who cannot express their distress. In that case, it is imperative to seek the advice of a pediatric otolaryngologist at the earliest onset of symptoms for an evaluation and potential treatment.
Determining when to seek medical attention for a child with ear infections is a significant concern, particularly for young children who cannot articulate their discomfort. However, there are specific indicators that can be used to identify an ear infection, including tugging or rubbing of the ear, increased fussiness, and a refusal to eat or drink. Should any of these symptoms be present, it may be necessary to seek medical attention. Furthermore, if fluid is observed coming from the ear, it is probable that your child is suffering from a middle ear infection and should receive prompt medical attention.
Prompt medical attention is critical as complications, such as ruptured eardrums, hearing loss, and developmental delays, can arise from untreated ear infections. Consequently, it is advisable to confer with a medical expert if the symptoms do not reduce within the suggested timeframe or if your child’s condition worsens.